KPMG survey on Canada’s adoption of generative artificial intelligence indicates the tools drive both quality and productivity gains.
An increasing number of Canadians are integrating generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools into their professional endeavors, as indicated by recent research conducted by KPMG in Canada.
According to KPMG’s survey encompassing 4,515 Canadians, nearly a quarter now utilize generative AI to facilitate their work—an upward trend from previous assessments. Notably, the frequency of usage has surged, with over 60% of generative AI users employing the technology multiple times weekly, a significant rise from the reported usage six months earlier. Moreover, one in five Canadians report employing generative AI on a daily basis for work-related tasks.
Seamus Blackmore, a partner at KPMG in Canada and a key figure in Lighthouse, the firm’s emerging technology practice based in Toronto, highlighted the rapid adoption rate. He emphasized how generative AI has not only transformed work methodologies but has also accelerated technological advancements, expediting breakthroughs across various domains.
Blackmore further elaborated on the evolution of generative AI systems, indicating their transition from text-based prompts to multi-modal capabilities, enabling content creation from images or voice commands. He emphasized the importance for business leaders to grasp the swift evolution of this technology, comprehend its potential impact on their enterprises, and adapt their strategies to remain competitive.
Blackmore highlighted a significant annualized growth rate of 32 percent in the adoption of this tool within the workplace, suggesting that half of Canada’s workforce could integrate it within three years.
“In its initial availability, professionals were exploring the capabilities of the tool, assessing its potential to enhance efficiency. However, our survey indicates that generative AI has evolved into a vital asset for numerous Canadian professionals. Over 90% of users affirm its positive impact on their work, with 70% deeming it essential in managing their workload,” he stated.
KPMG devised Canada’s inaugural Generative AI Adoption Index to gauge the prevalence of generative AI tool utilization within Canadian workplaces, aiming to comprehensively understand the technology’s implications for organizations and society.
The Index presently stands at 14.6, denoting a 28% growth rate since its introduction in May 2023. A score of 100 signifies widespread adoption.
As generative AI usage proliferates among Canada’s labor force, distinct trends in its workplace application have emerged. Users are increasingly vigilant about verifying AI-generated content’s accuracy and are more transparent with employers regarding their utilization of these tools.
Among respondents, 77% confirm that their employers are aware of their use of generative AI, while 55% consistently validate information generated by this technology. A striking 90% acknowledge that these tools have enriched their professional output, enabling 76% to undertake additional work they previously lacked capacity for.
Blackmore noted that as generative AI matures, users are gaining proficiency in leveraging its advantages, resulting in heightened productivity.
“Since the public introduction of generative AI a year ago with the advent of ChatGPT, users have honed their skills in formulating effective prompts, yielding swifter and improved outcomes. Consequently, they potentially gain a competitive edge at work, saving considerable time,” he remarked.
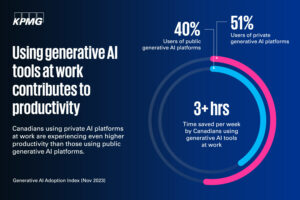
Surveys reveal that more than three-quarters of users rely on publicly available generative AI tools for their work, while the remaining quarter utilize private generative AI tools developed exclusively by their employers.
Interestingly, employees using private AI platforms report higher productivity gains compared to those using publicly available tools. Over half of those relying on private tools claim to save more than three hours of work per week, a figure slightly lower, at 40 percent, for users of publicly accessible platforms.
Marc Low, a director based in Vancouver at KPMG Ignition, the firm’s innovation lab, highlighted the growing prevalence of bespoke enterprise generative AI platforms, noting their increasing accessibility, affordability, and potency.
“As customizable tools become more widespread, we anticipate a rise in organizations adopting private generative AI systems. The more extensively employees utilize these tools, the more they stand to benefit,” he remarked.
Low underscored organizations’ interest in integrating private generative AI systems while acknowledging their hesitation, often stemming from the influx of new tools, frequent technology updates, and the evolving market landscape.
“The considerable buzz around generative AI can trigger serious FOMO (fear of missing out) among business leaders, prompting hasty decisions to keep pace with competitors. Yet, this rush can lead to poor choices and wasted investments,” he cautioned.
He advised organizations to conduct comprehensive assessments of how generative AI would impact their operations, advocating for structured experimentation within a specific business segment. Low also recommended exploring diverse generative AI tools and applications to validate their impact, value, and adoption.
“Embracing generative AI solely due to its popularity or peer adoption isn’t a prudent business approach. Organizations must be deliberate, defining why they need it, pinpointing areas of maximum impact, and devising metrics to measure productivity enhancements and competitiveness for a substantial return on investment,” he advised.